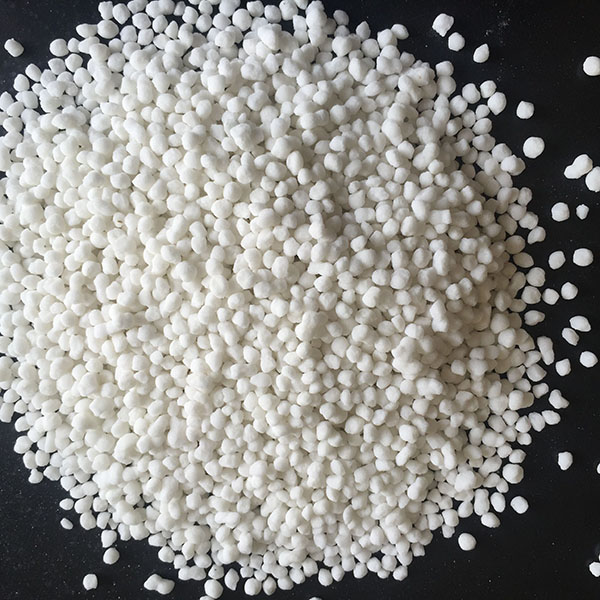
Ammonium Sulphate Granular(Steel Grade)

Nitrogen: 20.5% Min.
Sulphur: 23.4% Min.
Moisture:1.0% Max.
Fe:-
As:-
Pb:-
Insoluble: -
Particle Size: Not less than 90 percent of the material shall
pass through 5mm IS sieve and be retained on 2 mm IS sieve.
Appearance: white or off-white granular, compacted, free flowing, free from harmful substances and anti-caking treated
Appearance: White or off-white crystal powder or granular
●Solubility: 100% in water.
●Odor: No odor or slight ammonia
●Molecular Formula / Weight: (NH4)2 S04 / 132.13 .
●CAS No.: 7783-20-2. pH: 5.5 in 0.1M solution
●Other name: Ammonium Sulfate, AmSul, sulfato de amonio
●HS Code: 31022100










The primary use of ammonium sulfate is as a fertilizer for alkaline soils. In the soil the ammonium ion is released and forms a small amount of acid, lowering the pH balance of the soil, while contributing essential nitrogen for plant growth. The main disadvantage to the use of ammonium sulfate is its low nitrogen content relative to ammonium nitrate, which elevates transportation costs.
It is also used as an agricultural spray adjuvant for water-soluble insecticides, herbicides, and fungicides. There, it functions to bind iron and calcium cations that are present in both well water and plant cells. It is particularly effective as an adjuvant for 2,4-D (amine), glyphosate, and glufosinate herbicides.
-Laboratory Use
Ammonium sulfate precipitation is a common method for protein purification by precipitation. As the ionic strength of a solution increases, the solubility of proteins in that solution decreases. Ammonium sulfate is extremely soluble in water due to its ionic nature, therefore it can "salt out" proteins by precipitation. Due to the high dielectric constant of water, the dissociated salt ions being cationic ammonium and anionic sulfate are readily solvated within hydration shells of water molecules. The significance of this substance in the purification of compounds stems from its ability to become more so hydrated compared to relatively more nonpolar molecules and so the desirable nonpolar molecules coalesce and precipitate out of the solution in a concentrated form. This method is called salting out and necessitates the use of high salt concentrations that can reliably dissolve in the aqueous mixture. The percentage of the salt used is in comparison to the maximal concentration of the salt in the mixture can dissolve. As such, although high concentrations are needed for the method to work adding an abundance of the salt, over 100%, can also oversaturate the solution, therefore, contaminating the nonpolar precipitate with salt precipitate. A high salt concentration, which can be achieved by adding or increasing the concentration of ammonium sulfate in a solution, enables protein separation based on a decrease in protein solubility; this separation may be achieved by centrifugation. Precipitation by ammonium sulfate is a result of a reduction in solubility rather than protein denaturation, thus the precipitated protein can be solubilized through the use of standard buffers.[5] Ammonium sulfate precipitation provides a convenient and simple means to fractionate complex protein mixtures.
In the analysis of rubber lattices, volatile fatty acids are analyzed by precipitating rubber with a 35% ammonium sulfate solution, which leaves a clear liquid from which volatile fatty acids are regenerated with sulfuric acid and then distilled with steam. Selective precipitation with ammonium sulfate, opposite to the usual precipitation technique which uses acetic acid, does not interfere with the determination of volatile fatty acids.
-Food additive
As a food additive, ammonium sulfate is considered generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, and in the European Union it is designated by the E number E517. It is used as an acidity regulator in flours and breads.
-Other uses
In the treatment of drinking water, ammonium sulfate is used in combination with chlorine to generate monochloramine for disinfection.
Ammonium sulfate is used on a small scale in the preparation of other ammonium salts, especially ammonium persulfate.
Ammonium sulfate is listed as an ingredient for many United States vaccines per the Centers for Disease Control.
A saturated solution of ammonium sulfate in heavy water (D2O) is used as an external standard in sulfur (33S) NMR spectroscopy with shift value of 0 ppm.
Ammonium sulfate has also been used in flame retardant compositions acting much like diammonium phosphate. As a flame retardant, it increases the combustion temperature of the material, decreases maximum weight loss rates, and causes an increase in the production of residue or char.[14] Its flame retardant efficacy can be enhanced by blending it with ammonium sulfamate.[citation needed] It has been used in aerial firefighting.
Ammonium sulfate has been used as a wood preservative, but due to its hygroscopic nature, this use has been largely discontinued because of associated problems with metal fastener corrosion, dimensional instability, and finish failures.